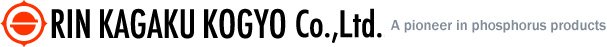Fire retardants
"Fire retardants" are materials with properties so that when they mixed with raw materials that burn easily (such as plastic, rubber, wood, fabric or paper), or coated onto these materials, they make the material less likely to burn, and prevent the flame from spreading.
The features of red phosphorus fire retardants
Red phosphorus is a highly combustible hazardous material, which is used in the striking surface for matches. However, when a small amount of red phosphorus is mixed with a flammable resin, the resin becomes less likely to burn.
The mechanism by which plastic becomes less flammable
1) When the resin burns it combines with the oxygen in the air to produce carbon dioxide, water and soot (carbon).
CmHm + O2 → CO2 + H2O + C
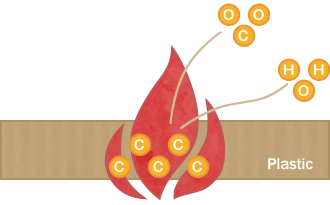
2) Red phosphorus combines with the oxygen and water in the air to produce condensed phosphoric acid (a polymer of phosphoric acid).
P + O2 + H2O → (HPOx)n condensed phosphoric acid
3) The soot (carbon) produced in step 1) mixes with the condensed phosphoric acid produced in step 2)
to form a thin film on the surface of the plastic.
This film, known as "char," keeps the oxygen out, so that the flame goes out.

The features of red phosphorus fire retardants
There are several types of fire retardants, including fire retardants based on halogen and
metal hydroxides.
Red phosphorus fire retardants have the following advantages compared to these alternatives.
(ⅰ)Fire retardant effects obtained with small quantities
Red phosphorus fire retardants contain large amounts of the phosphorus (P) required for the
formation of condensed phosphoric acid in Step 2) of "The mechanism by which plastic becomes less
flammable." Moreover, phosphorus is the element with the most fire retardant effect among all elements so
that it can efficiently obtain a fire retardant effect with small quantities.
This makes it possible to minimize the degradation of the physical properties of the resin.
Comparison of fire retardant effects
| PP | PE | PA6 | PA66 | PC | PBT | EP | PF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroxide metal | 25 | 65 | 50 | - | - | - | 150 | - |
| Glass fiber | - | - | - | 50 | - | - | - | - |
| Silica | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 763 |
| Red phosphorus fire retardant | 5 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 15 | 9 |
| Polyurethane resin | - | 4 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Phenol resin | - | - | - | 20 | - | 20 | - | - |
| Hardener | - | - | - | - | - | - | 90 | - |
| Expandable graphite | 10 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Solvent | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 80 |
| Other | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1.8 |
| Fire resistance UL94 (1/16) * | V-0 | V-0 | V-0 | V-0 | V-0 | V-0 | V-0 | V-0 |
* Index relative to 100 parts of resin. 1/16 is the thickness (in inches) of the test piece.
Electrical properties of fire retardant resin
The following table shows data for the electrical properties for each of
the cases when RINKA_FR, RINKA_FE and untreated red phosphorus are added
to plastic.
As for compositions which added RINKA, the degradation of the volume resistance
can be minimized.
These data are some representative figures, and they do not guarantee the
quality of product.
| Epoxy resin | Amount added (phr)* | Volume resistivityρ(Ω・cm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ρ0 | ρ2000hr | ||
| Untreated red phosphorus | 15 | 1.9×1016 | 7.8×109 ** |
| RINKA _FR120+Aℓ(OH)3 | 10+100 | 2.4×1015 | 1.7×1013 |
| RINKA _FE140+Aℓ(OH)3 | 10+100 | 3.7×1015 | 6.1×1013 |
| Aℓ(OH)3 | 120 | 2.8×1015 | 1.1×1012 |
| No additives | ― | 3.0×1015 | 5.5×1014 |
Volume resistivity 500V.DC/min(70℃、93%RH)
* :Amount added per 100 parts of resin
** :1000hr for untreated red phosphorus only
(ⅱ)Low toxicity and excellent safety
Red phosphorus is an effectively harmless substances with extremely low toxicity.
Phosphine is included in the combustion gases in a fire, but phosphine has been shown to have relatively
low toxicity. (See "The environmental impact of red phosphorus fire retardants")
Moreover, the quality can be stabilized by coating red phosphorus with resins and so on, making it easier
to handle than untreated red phosphorus.
Humidity resistance
Our red phosphorus products have also been improved in terms of phosphine emissions and degradation of electrical properties.
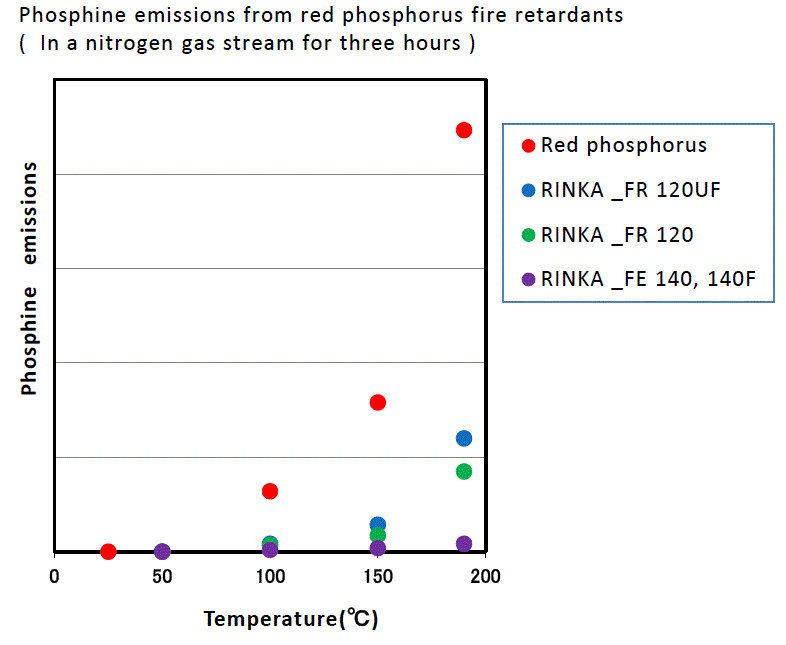
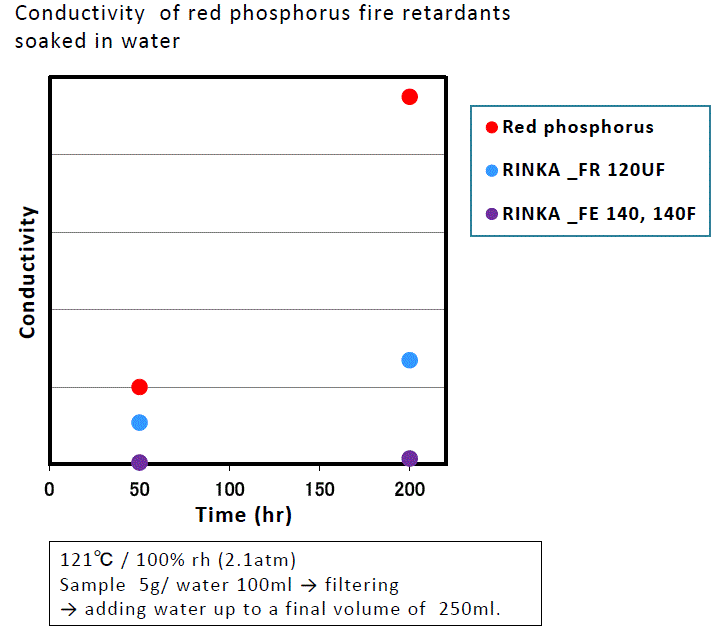
These data are some representative figures, and they do not guarantee the quality of product.
Temperature of spontaneous combustion
RINKA_FR and RINKA_FE are both more stable than untreated red phosphorus,
having higher temperature of spontaneous combustion.
These data are some representative figures, and they do not guarantee the
quality of product.
・Untreated red phosphorus : 250~260℃
・RINKA_FR : 300~350℃
・RINKA_FE : 300~350℃
Blow ignition characteristics
RINKA_FR and RINKA_FE have decreased blow ignition characteristics in comparison
with untreated red phosphorus, and RINKA_FQ has decreased blow ignition
characteristics more.
These data are some representative figures, and they do not guarantee the
quality of product.
| Height(cm) | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | ~ | 100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated red phosphorus | × | ○ | |||||
| RINKA _FR 120 | × | × | ○ | ||||
| RINKA _FE 140 | × | × | ○ | ||||
| RINKA _FQ ST100 | × | × | × | × | × | × | |
| RINKA _FQ RX | × | × | × | × | × | × |
Test method: Find the shock combustion point by placing a 1g sample in a mortar and dropping
a pestle onto the sample, varying the height of the pestle. (Both the mortar and the pestle are made of
steel, and the mass of the pestle is 1.8kg)
○ symbol: combustion; ×symbol: no combustion
(ⅲ) Better fire retardant performance as a result of synergistic effects
Even higher fire resistance can be achieved by using red phosphorus together with other fire
retardants, particularly fire retardants based on metal hydroxides with strong endothermic
properties.
These data are some representative figures, and they do not guarantee the quality of product.
| Resin | RINKA_FR (phr)*1 |
Metal hydroxide (phr)*1 |
OI | Fire resistance UL94 (1/8)*2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVA | 0 | 0 | 21 | HB |
| 5 | 0 | 23 | V-2 | |
| 0 | 100 | 24 | V-2 | |
| 5 | 100 | 50 | V-0 | |
| PP | 0 | 0 | 19 | HB |
| 10 | 0 | 20 | V-2 | |
| 0 | 150 | 29 | HB | |
| 10 | 150 | 38 | V-0 |
*1 Index relative to 100 parts of resin
*2 1/8 is the thickness (in inches) of the test piece.